The laboratories are back bone of any industries as they provide a robust foundation for all research activities as well as to control the quality of the products that industries produce. Due to this companies invest millions of dollars in setting up laboratories before they set up any manufacturing plants. The Laboratory designs have evolved over the period. Modern laboratories not only provide the basic experimental study platform for scientists & chemists but also help brightest minds to collaborate & propel the industrial growth benefitting mankind.
As working practices have changed over the years, with technology and increased automation changing the way scientists work; science laboratory design has also changed significantly. Modern labs need to be capable of responding and adapting to the needs of the team, whether a project requires collaboration, wet lab work, or computer analysis. This has led to a growing diversity in lab design, from flexible labs that can be completely altered depending on the needs of the team to fixed-purpose specialist labs that are carefully designed for one field of research.
Fires and explosions are major contributors to loss of life and property in laboratories. A study of one hundred significant laboratory fires by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA- USA) provides some interesting facts: 71% of the fires originated in the laboratories; 56% of the laboratory fires originated between 6 PM and 6 AM; 67% of the fires were caused by:
- Electrical equipment (wire and appliances) 21%
- Misuse of flammable liquids 20%
- Explosions 13%
- Gas 7%
- Spontaneous ignition 6%
Since millions are being invested in setting up the laboratories & considering the critical importance of these facilities, it becomes very much important to protect these facilities from any kind of hazards not only to protect the costly facilities, instruments but also to protect the finest brains from the industry.
With minimum precautions & specific approach we can integrate the safety right from the concept planning stage of these facilities so that we can mitigate the risk to great extent if not eliminate it completely. This article further describes how we can ensure Safety by Design while building or renovating the laboratory facilities.
Design Considerations
Laboratory users involved in the predesign or design phase of a research laboratory project often know what features their future laboratory must have but it may not directly get translated into design requirements. This is because lab users may not necessarily have an experience in laboratory design and may be unfamiliar with design issues, possible design alternatives, or methods of evaluating those alternatives. This is where the designers must strike a right balance between user expectations & design optimization without compromising the basic functionality or safety of lab & also keeping the operating costs in check to make the operations commercially viable.
While some of the design approaches discussed in this article may require increase in construction and operation costs, they are critical to the functionality of the facility and the safety of the building users and surrounding community. Users’ familiarity with alternative approaches to specific laboratory design issues will most likely lead to a more efficient, cost-effective, flexible, safe, and environmentally appropriate laboratory facility. Although an experienced and knowledgeable design professional can assist in the identification of design issues to consider and can evaluate appropriate alternative approaches to laboratory design, this is not always the case. Even when an experienced and knowledgeable design professional is available, it is advantageous for the user representative and the client team to become informed consumers of the design professional’s services.
Laboratory Designers, particularly Architects/Engineers must work closely with end users to get aligned themselves with the functional requirements of laboratories & to understand the process flow to make designs more efficient & convenient for the users.
Essentially any laboratory design shall begin with detailed Risk Assessment. The Risk Assessment must address following key issues –
- Building Footprint & Surrounding Occupancies
- Renovation V/S New Construction
- Floor Plan & Floor Heights
- Construction Material Selection
- Men & Material Movement
- Exhaust Ventilation
- Electrical Distribution
- Seismic Consideration
- Services Distribution
- Hazardous Material Storage & Handling
- Fume Hoods
- Chemical Storage & Handling
- Emergency Equipment Such as Eyewash & Shower
- Fire Detection & Suppression System
- Chemical/Biological Containment/ Bio Safety & Bio Security
- Solid/Liquid Waste Disposal
- Gas Distribution System
- Pressure Vessels & Compressed Gas storages
- Gas Leak Detection Systems
- Solvents Storage & Handling
- Fireproof Storage Cabinets
- Laboratory Furniture & Corresponding Ergonomic Issues
- Cryogenic Storages/Liquid Nitrogen Handling
- Chemical/Biological Containment Devices such as Bio-Safety Cabinets
- Ionizing & Non-Ionizing Radiation Control
- Special Flooring Requirements such as Anti-Static Flooring
- Change Rooms & Office Areas duly Separated
- Emergency Exit Paths
- Fire Lifts/fire Towers
- Laboratory Lighting
- Laboratory Utilities such as Water, Steam, Gases, Vacuum, Compressed Air etc.
- Laboratory Access Control/ CC TV & Public Address
- Sustainable Designs & Energy Management
- Internet of Things (IOT) Compatibility
- Machine Guarding & Warning Signs
- Lock Out / Tag Out
- Special Areas Such as Dark Rooms/ Animal Rooms etc.
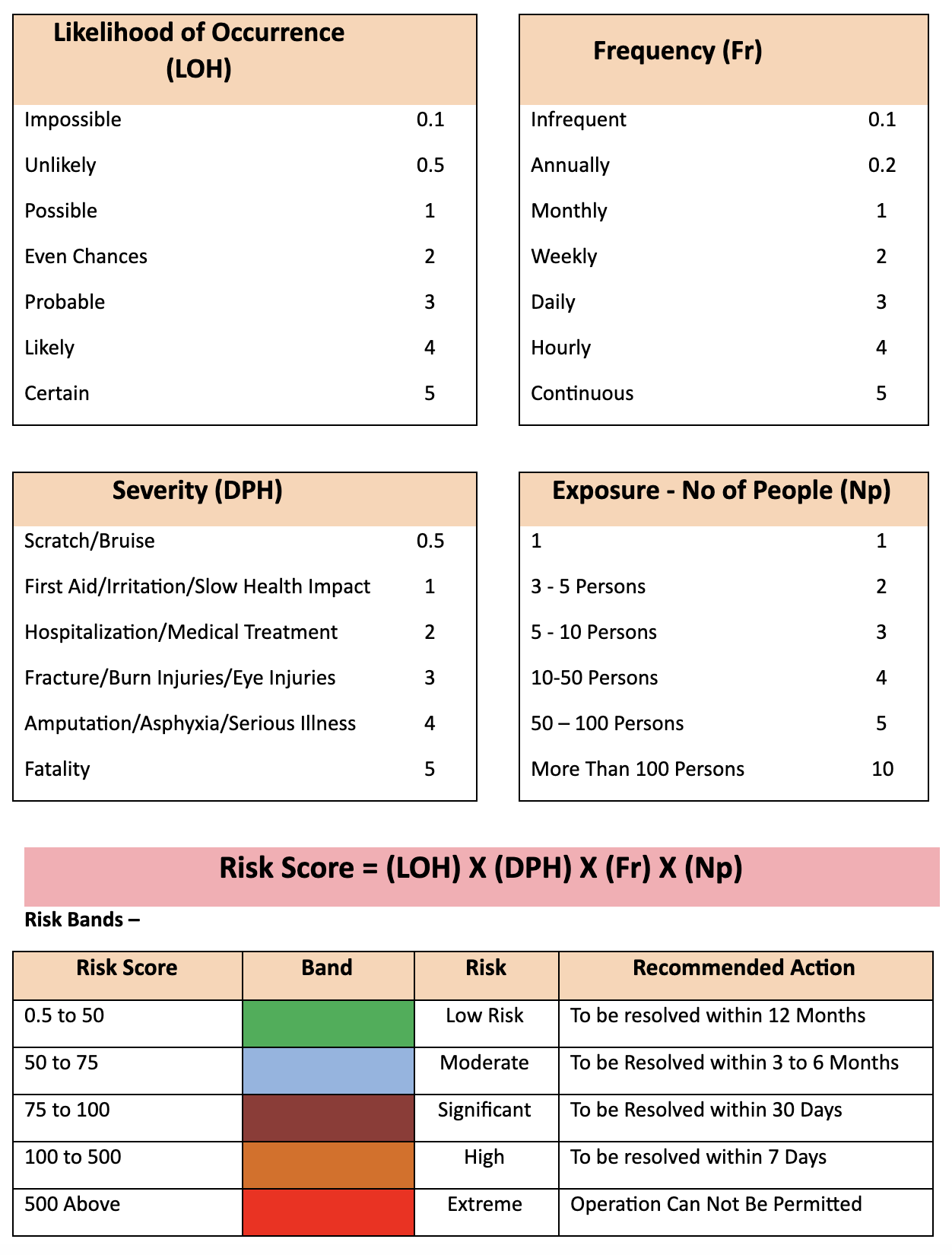
Risk Assessment Guide
A below tool shall help designers to identify the hazards & conduct the risk assessment so that they can deploy most appropriate Risk Mitigation Strategy for their project. The designers need to first Map their process in detailed. Subsequently they shall break down each line operation into a smaller work steps to perform the Job Safety Analysis with tool given below.
Modern Design Techniques
Now a days due to advancement of technology it is possible for designers to use various software & design tools through which they can simulate many scenarios virtually to test the correctness of their designs much before they go for actual construction stage. This makes them much more confident in designing the facilities & avoid potential design deficiencies or failures at later stages. This also helps designers to avoid costly reworks & more importantly protect the facilities from any potential failures or disasters arising out of any design inadequacies. Few of these techniques include –
Building Information Modelling
Building Information Modelling (BIM) is an intelligent 3D model-based process that gives architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) professionals the insight and tools to more efficiently plan, design, construct, and manage buildings and infrastructure. This tool allows designers to virtually construct the building in real time manner before they hit the ground. This tool also helps designers to control their project budget effectively due to an extra-ordinary control on the BOQ generations.
Computational Fluid Dynamix
Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is a branch of fluid mechanics that uses numerical analysis and data structures to analyse and solve problems that involve fluid flows. This tool can help designers to understand thee air flow patterns while designing the facilities which require high containment such as in Oncology or BSL-4 facilities.
Key Components of the Lab of the Future
Flexibility
Users always prefer their labs to be flexible. The flexibility applies to the building, lab space, shared areas, casework, equipment and furniture. Modular furniture & Modular partitions are the order of the day in lab designs.
Versatility
Users want their workplaces to be versatile or multifunctional so that they do not have to keep moving from one place to another to carry out their routine tasks. Gone are the days when labs use to be dedicated for a fixed operation or purpose.
Technology
Users prefer to maximize the use of technology in their workplaces so that it can ease up their routine tasks & help them balance their Work-Home lives. IOT is bringing in paradigm shift in the way people work now.
Collaboration
Internet has brought the world very close. The research activities are mainly driven by the collaborative efforts between different people & teams without boundary of their locations, regions, countries or continents. Hence provision of collaborative platform such as huddle rooms, tele/video conferencing facilities are the new norms in laboratory designs where people can share & plan their activities together.
Mobility
Use of mobile equipment in lieu of fixed, so it can be stored in an equipment or storage room.
Safe Workplaces
Safety is always a priority and is a component of any good lab design. Appropriate safety equipment for each type of lab needs to be considered such as showers, eye washes, goggle cabinets, first aid kits, ventilation, storage, spill control kits etc. An often-overlooked safety component is access to the equipment due to room layout and designs. Designers must thoroughly pay an attention to the workplaces designs in order to provide the best ergonomics & safest work environment to lab workers.
Sustainable Designs
The modern buildings must be deigned with aim at keeping it carbon negative & water positive as much as possible, so that they drive growth by causing minimum damage to an environment.
Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) was developed by the U.S. Green Building Council (USGBC) to encourage environmental responsibility and efficient use of resources. Even if your project is not going to be a LEED project, it is wise to give serious consideration to green building design, as it will affect planning, design, construction and operation of the new facility.
There are new green advances in lab equipment as well with fume hoods leading the way. The latest development is a ductless chemical fume hood, but it is not for everyone. There are other fume hood options that are energy efficient and can save energy and money.
Courtsey – Ajit Kadam, Director, Spectrum Pharmatech Consultants Pvt. Ltd.
